Companies that process raw metal material into usable products are known as metal fabricators. The term metal fabrication is a unique and markedly unspecific one that, in this context, refers to the entire process of creating metal products using any number of metalworking processes. In a sense, the significance of the words metal fabrication lies in the commercial structure that typically underlies the process. Read More…
A premier custom stainless steel fabricator solving complex challenges since 1951. We are a one-stop-shop offering advanced laser cutting (flat, tube, 5-axis), precision forming, and certified welding (GTAW, laser, robotic). We are ISO 9001:2015 certified and experts in stainless steel, duplex, and high-nickel alloys like Hastelloy.

At MET Manufacturing Group, we take pride in our expertise in metal fabrication, where precision, innovation, and craftsmanship come together to create durable and high-quality components. We specialize in transforming raw metal into complex parts and assemblies that serve a wide range of industries, from construction and transportation to energy and manufacturing.

At Kalamazoo Fabricating, we take pride in delivering high-quality metal fabrication solutions that bring precision, strength, and innovation to every project we undertake. We specialize in transforming raw materials into fully engineered components, assemblies, and structures that meet the exacting standards of our customers across diverse industries.

At Anchor Fabrication, we take pride in being a trusted partner for comprehensive metal fabrication solutions that serve a wide range of industries. We bring precision, efficiency, and craftsmanship to every project, combining advanced technology with years of hands-on expertise.

Accurate Metal Fabricating has been providing metal fabrication to OEM's and job shops for over 80 years. We fabricate, engineer, and perforate to the most precise specifications for the most demanding companies. We offer a full range of metal customization and fabrication capabilities that bring your design to reality. Our abilities range from forming and laser-cutting to powder coating and...

At Victory Machine & Fab, we take pride in delivering high-quality metal fabrication solutions that combine precision craftsmanship with advanced technology. We specialize in transforming raw materials into functional, durable, and custom-engineered components that meet the highest industry standards.

More Metal Fabrication Companies
Metal fabricators are specialized companies that transform raw metal materials into usable products, components, or assemblies for a wide range of industries. The term metal fabrication broadly encompasses the entire process of producing metal goods through various metalworking techniques, including cutting, bending, welding, and finishing. The importance of metal fabrication lies in its pivotal role within the commercial and industrial manufacturing sectors, where it enables the creation of custom and standardized metal products for construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, and many other applications. Whether you are searching for custom metal fabrication, contract manufacturing, or specialized sheet metal fabrication services, understanding the nuances of this field can help ensure you partner with the right metal fabrication company for your project.
What is Metal Fabrication?
Metal fabrication involves transforming raw metal materials into finished, usable products through a series of processes such as cutting, shaping, bending, assembling, and surface finishing. These processes may be manual, automated, or a combination of both, depending on production requirements and precision needs.
Typically, metal fabrication shops are centralized facilities equipped with a variety of metalworking tools and technologies, enabling them to handle complex fabrication projects from start to finish. These shops employ skilled specialists in different areas of metallurgy, such as certified welders, blacksmiths, CNC machine operators, and sheet metal technicians. Common metalworking processes within a metal fabrication project include casting, bending, stamping, welding, punching, CNC machining, shearing, rolling, and forging. It’s important to note that while metal fabrication and welding are closely related, welding is just one phase within the broader metal fabrication workflow.
Common Materials Used in Metal Fabrication
Nearly any metal or metal alloy can be utilized to create a product or part of a product, but certain materials are more commonly chosen than others. Steel, stainless steel, and aluminum are the primary materials used in metal fabrication. Other frequently used metals include bronze, brass, copper, and titanium, each offering unique properties that make them suitable for specific applications. For instance, stainless steel is favored for its corrosion resistance and shiny appearance, making it ideal for food processing equipment, medical devices, and decorative architectural features. Galvanized steel (steel coated with zinc) is a cost-effective option for outdoor structures due to its rust-resistant properties. Similarly, copper is prized for its electrical conductivity and visual appeal, while aluminum is chosen for its lightweight, high strength-to-weight ratio, and natural resistance to corrosion.
Fabricated metal products are rarely made from freshly mined, unprocessed metals. Instead, they are typically fabricated from pre-processed or semi-finished metal materials. The standard raw materials used by metal fabricators include sheet metal (referred to as plate metal when its thickness reaches a quarter-inch), tube stock, bar stock, welding wire or welding rod, formed and expanded metal, metal castings, and a variety of metal fittings. Each raw material form offers distinct advantages for different fabrication methods. For example, CNC machining is often performed on solid bar or tube stock for high-precision parts, while sheet metal fabrication is favored for creating enclosures, panels, and brackets due to its versatility and ease of forming.
Main Stages of Metal Fabrication
To create various products from different types of raw materials, metal fabricators rely on a wide range of processes. The primary methods of metalworking are detailed below. While it may be an oversimplification, most metal fabrication projects can be categorized into four main stages: cutting, shaping (often involving bending and forming), assembling or joining (primarily through welding), and finishing.
1. Cutting
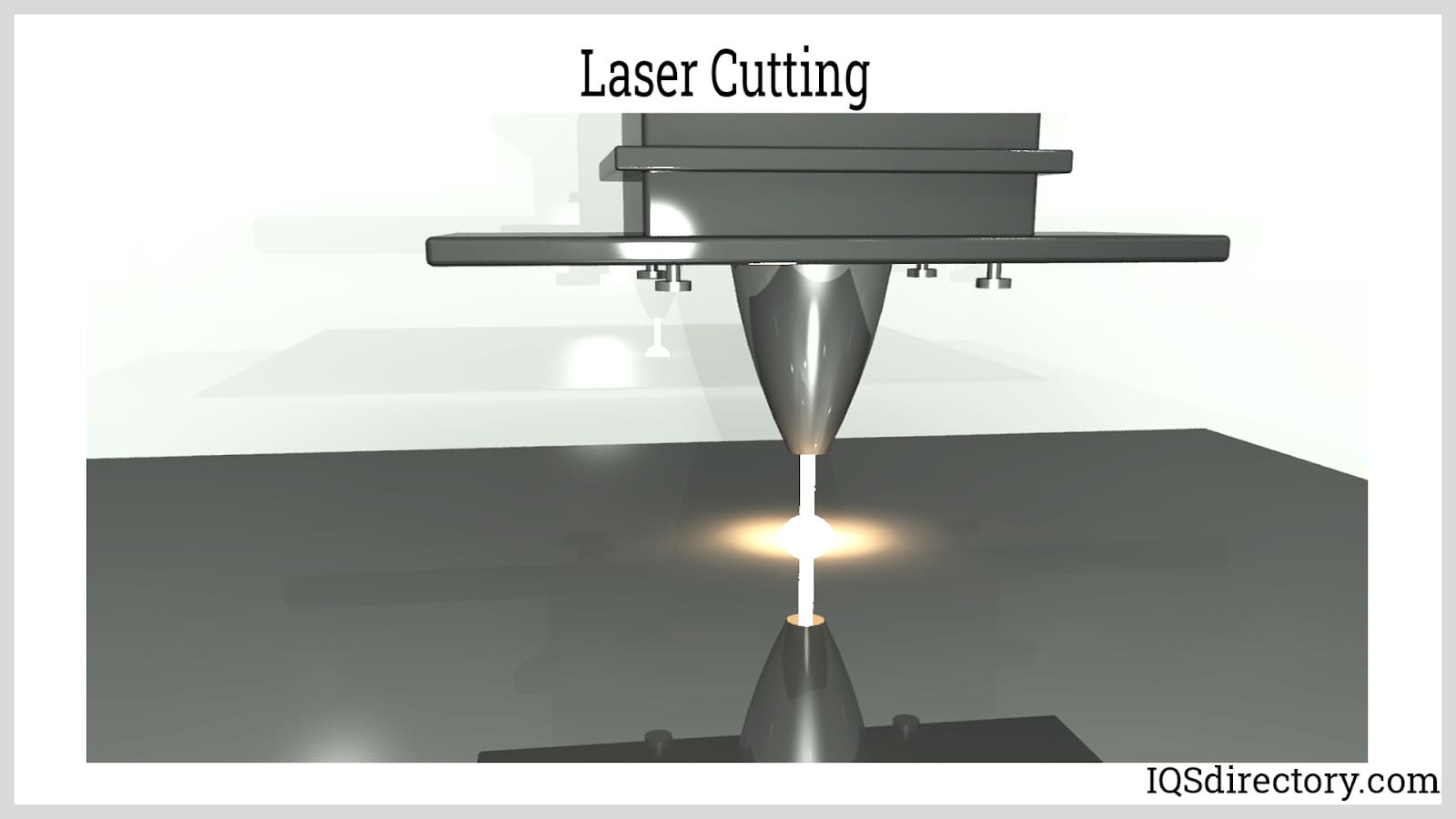
Cutting is the initial step that transforms raw metal into a workable size or shape. This may be done manually with hand tools or with advanced, automated equipment such as CNC laser cutters, plasma cutters, or waterjet machines. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machinery is especially valued for its precision and ability to handle complex geometries in both high-volume and custom fabrication projects. When working with sheet or sectional metal, cutting typically involves shear cutting operations like shearing (removing large parts of the stock with a shearing blade), punching (creating holes in the stock with a punch mechanism), and blanking (removing the perimeter from the stock). Non-shear operations, such as laser cutting, waterjet cutting, and plasma cutting, offer higher precision and cleaner edges, making them ideal for intricate work and tight tolerances.
2. Shaping and Forming
The intermediate step of metal fabrication, often termed shaping or metal forming, involves transforming metal and metal components into a desired shape after they have been properly cut. This is usually achieved with dies and presses, which hold the raw material in place as it is worked. Stamping presses, for example, use dies and punches to form coiled or blank sheet metal into a net shape. Common shaping and forming processes include:
- Embossing – Stretching the material into a hollow depression for decorative or functional purposes.
- Flanging – Bending the material along a curved line to add strength or allow for assembly.
- Coining – Compressing or imprinting a pattern into the material for surface texture or identification.
- Bending – Deforming the material along a straight line, often with press brakes or manual tools.
Some projects may require roll forming, a continuous, high-volume process where metal strips are passed through a series of rollers to create products like channels, trim, and rails. Press braking is better suited for smaller production runs or custom shapes, using a press brake machine to force metal into a shaped indentation for precise bends.
3. Assembling or Joining
Assembling or joining is a crucial stage in the metal fabrication process, where multiple metal parts are fused or fastened together to create a finished product or sub-assembly. Before assembly, metal pieces are held in place with clamps and fixtures to ensure accuracy. Assembly techniques include mechanical fastening (using adhesives, threaded fasteners, or riveting), brazing, and, most commonly, welding. Welding forms the strongest bonds between metal parts and is essential for structural steel fabrication, industrial equipment, automotive components, and more.
Welding processes can derive heat from various sources, including friction, ultrasound, gas flames, electron beams, electric arcs, and lasers. Common welding methods include:
- Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW)
- Flux-cored arc welding (FCAW)
- Submerged arc welding (SAW)
- Electroslag welding (ESW)
- Electric resistance welding (ERW)
- Oxyacetylene welding (OAW)
- Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) – including metal inert gas (MIG) welding and metal active gas (MAG) welding
- Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) or tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding – highly valued for its precision and clean welds
Welding is so versatile and critical that advanced processes have been developed for unique applications, such as underwater welding for marine structures and aerospace welding for spacecraft and satellites. Beyond these specialized fields, welding remains a cornerstone of industrial manufacturing, automotive fabrication, energy production, and infrastructure construction.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage of metal fabrication involves enhancing the surface properties of metal products, either to fortify them against environmental damage or to improve their aesthetic appeal. Common finishing techniques include:
- Cleaning and degreasing with organic solvents (like acetone) or alkaline solutions
- Painting or powder coating for improved corrosion resistance and color customization
- Anodizing (especially for aluminum) to create a protective oxide layer
- Electroplating to deposit a metal layer (such as chrome or nickel) for enhanced wear resistance or conductivity
- Polishing, brushing, or sandblasting for desired surface textures or finishes
Finishing processes are often tailored to the end-use environment of the product, whether that means protecting against weather, chemicals, or abrasion, or simply meeting strict cosmetic requirements for consumer goods.
For every metalworking request, metal fabricators have a method to fulfill it. Through cutting, burning, forming, machining, welding, and related fabrication services, metal fabrication shops can provide customers with a wide variety of standard and custom fabricated parts. If you need rapid prototyping, small-batch manufacturing, or full-scale production, a qualified metal fabrication company can help you achieve your project goals.
Applications of Metal Fabrication
Metal fabricators’ services are indispensable across diverse commercial, industrial, and consumer markets. In commercial settings, fabricated metal parts and products are integral to items such as:
- Office furniture and fixtures (desks, chairs, paper trays, shelving)
- HVAC components, including ductwork, grating, and ventilation systems
- Store fixtures, display racks, and signage
- Architectural metalwork for buildings and public spaces
Within industrial and manufacturing environments, metal fabrication is essential for producing:
- Bent metal hoods for fluorescent lighting
- Stamped metal racks and bins
- Welded staircases, ladders, and hand railings
- Machine guards and enclosures
- Factory automation components
The automotive industry heavily relies on metal fabrication for:
- Vehicle frames, trim, and body panels
- Engine brackets, exhaust systems, and mounting hardware
- Custom car parts and performance upgrades
In the construction sector, fabricated metal products include:
- Structural steel beams and columns
- Bridge skeletons and supports
- Heavy machinery components
- Handrails, stair treads, and safety grates
Even in residential settings, metal fabrication plays a vital role in everyday life. Examples include:
- Appliances (refrigerators, ovens, washing machines)
- Kitchenware (pots, pans, cutlery)
- Furniture (bed frames, table bases)
- Decorative items (jewelry, lighting fixtures)
- Pet cages and home storage solutions
Emerging sectors such as aerospace, renewable energy, and electronics also depend on advanced metal fabrication for:
- Aircraft frames, engine mounts, and landing gear
- Wind turbine components and solar panel frames
- Computer hardware enclosures, heat sinks, and small electronic housings
- Precision-engraved parts and microfabricated assemblies
Benefits of Professional Metal Fabrication Services
Choosing a professional metal fabrication company provides numerous benefits, including:
- Custom engineering and design support – Tailored solutions for unique product requirements
- Quality assurance – Adherence to industry standards and certifications for safety and consistency
- Advanced technology – Utilization of CNC machining, laser cutting, robotic welding, and automated assembly for precision and repeatability
- Material expertise – Guidance in selecting the best metals and alloys for each application
- Cost efficiency – Lean manufacturing methods to minimize waste and maximize value
- Scalability – Capability to handle everything from one-off prototypes to high-volume production runs
- Rapid turnaround – Quick lead times for urgent projects and just-in-time manufacturing
When evaluating potential suppliers, consider their track record, customer reviews, capabilities, and willingness to collaborate on design improvements. A reputable metal fabrication partner will help you optimize costs, minimize lead times, and enhance product performance.
Safety Precautions in Metal Fabrication
While metal fabrication shops are highly valuable, they can also present significant safety hazards due to the use of heavy machinery, high temperatures, sharp edges, and hazardous materials. Effective safety management is essential to protect workers and maintain productivity. Standard safety precautions in these environments include:
- Wearing appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE): flame-resistant clothing, heavy aprons, steel-toed boots, leather gloves, safety goggles, face shields, and respiratory masks
- Practicing safe handling: Avoiding direct contact with cut metal edges, even when wearing gloves, to prevent lacerations
- Maintaining a clean, clutter-free work environment: Reducing hazards by removing excess metal scrap, oily residues, and wet surfaces
- Defining clear storage and tool management policies: Ensuring all manual and automatic tools are stored in designated locations when not in use
- Conducting regular equipment inspections: Identifying and addressing mechanical issues early to prevent accidents and equipment failure
- Immediately replacing or upgrading defective tools or machine parts: Especially critical for high-precision equipment like CNC machines and cutting lasers
- Implementing machine guarding and lockout/tagout procedures: Preventing accidental machine startups during maintenance or repair
Considerations for Selecting a Metal Fabrication Company
Engaging the services of a reputable metal fabrication shop is a wise investment for businesses seeking improved speed, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness in their metalworking projects. However, not all metal fabricators are created equal. When searching for a quality fabrication partner, consider the following decision factors:
- Capabilities: Does the company offer a comprehensive range of services, from design and prototyping to finishing and assembly? Can they handle your required materials, tolerances, and production volumes?
- Reputation: What do customer reviews and industry references say about their work quality, reliability, and client service?
- Certifications: Are they certified to relevant industry standards (such as ISO 9001, AWS, or ASME) that guarantee process control and product safety?
- Lead times and flexibility: How quickly can they deliver prototypes, small batches, or high-volume orders? Are they equipped for rapid changes or design iterations?
- Engineering support: Do they offer design-for-manufacturability (DFM) guidance to optimize your products for cost, performance, and manufacturability?
- Customer service: Is the fabricator responsive, transparent, and proactive in communication? Will they collaborate closely with your team throughout the project?
- Value-added services: Do they provide secondary operations like powder coating, assembly, logistics, or inventory management?
The success of a metal fabrication project heavily relies on the quality of initial layouts and designs. Therefore, it’s crucial to partner with a fabricator who invests the necessary expertise and time in the project’s early stages. A good metal fabricator will help you make decisions that optimize the overall fabrication process and meet your specific commercial needs. For example, a quality fabricator might advise against welding if it’s unnecessary, suggesting riveting or bonding instead. While welding is common, these alternatives can be preferable if ease of replacing damaged parts is a priority.
Frequently Asked Questions about Metal Fabrication
- What is the difference between custom metal fabrication and contract manufacturing?
Custom metal fabrication focuses on producing unique, made-to-spec parts or assemblies, often in small batches or one-off projects. Contract manufacturing, on the other hand, involves outsourcing large-volume production runs of standard or semi-custom components to a dedicated metal fabricator. - How do I select the best metal for my application?
Consider factors such as strength, weight, corrosion resistance, machinability, cost, and suitability for finishing. For structural applications, steel is often preferred for its high strength, while aluminum is ideal for lightweight or corrosion-resistant needs. Stainless steel is often chosen for hygiene or decorative requirements. - What is the lead time for a typical metal fabrication project?
Lead times vary based on project complexity, material availability, design changes, and production volumes. Simple parts may be completed in days, while intricate assemblies could take weeks. Early engagement with your fabricator and clear communication can help minimize delays. - Can metal fabrication shops handle both prototyping and full-scale production?
Yes, most modern metal fabrication companies offer rapid prototyping as well as scalable manufacturing services, ensuring continuity from initial concept to finished product. - What quality standards should I expect?
Look for fabricators that comply with ISO 9001, AWS D1.1, ASME, or other relevant certifications. These standards ensure process consistency, product safety, and traceability.
Summary: The Value of Metal Fabrication in Modern Manufacturing
Metal fabrication is a foundational process in modern manufacturing, supporting industries from construction and automotive to electronics and aerospace. By leveraging advanced technology, material expertise, and skilled labor, metal fabricators turn raw materials into the high-quality products and components that power our world. Whether you need custom sheet metal parts, large-scale structural steel fabrication, or rapid prototyping of precision assemblies, choosing the right metal fabrication partner is essential for achieving your project goals on time and within budget.
Ready to get started? Browse our directory: Find Trusted Metal Fabrication Companies Near You
What is metal fabrication?
Metal fabrication is the process of transforming raw metal materials into finished products by cutting, bending, shaping, assembling, and finishing. This can be accomplished using manual or automated tools and encompasses a variety of metalworking techniques.
Which materials are commonly used in metal fabrication?
The most commonly used materials in metal fabrication are steel, stainless steel, and aluminum. Other popular metals include copper, brass, bronze, galvanized steel, and titanium, each chosen for specific applications based on their properties.
What are the main stages of the metal fabrication process?
The primary stages of metal fabrication include cutting, shaping and forming, assembling or joining, and finishing. Each stage utilizes specialized tools and techniques to achieve the required result for the finished product.
What industries benefit from metal fabrication services?
Metal fabrication is essential for industries such as construction, automotive, aerospace, electronics, commercial manufacturing, and even residential products. It is also critical in emerging sectors including renewable energy and high-tech electronics.
How do I choose the right metal fabrication company?
To select a metal fabrication company, consider their range of services, certifications, reputation, engineering support, customer service, and ability to handle your materials, tolerances, and production volumes. Reviewing their industry standards compliance is also important.
What safety precautions are taken in metal fabrication shops?
Safety in metal fabrication shops is maintained by using personal protective equipment (PPE), keeping work areas clean, establishing clear tool management, regularly inspecting equipment, and following machine guarding and lockout/tagout procedures.
What are the benefits of working with a professional metal fabrication service?
Professional metal fabrication services offer custom engineering, quality assurance, advanced technology, material expertise, cost efficiency, scalability, rapid turnaround, and the ability to provide tailored solutions for diverse applications.






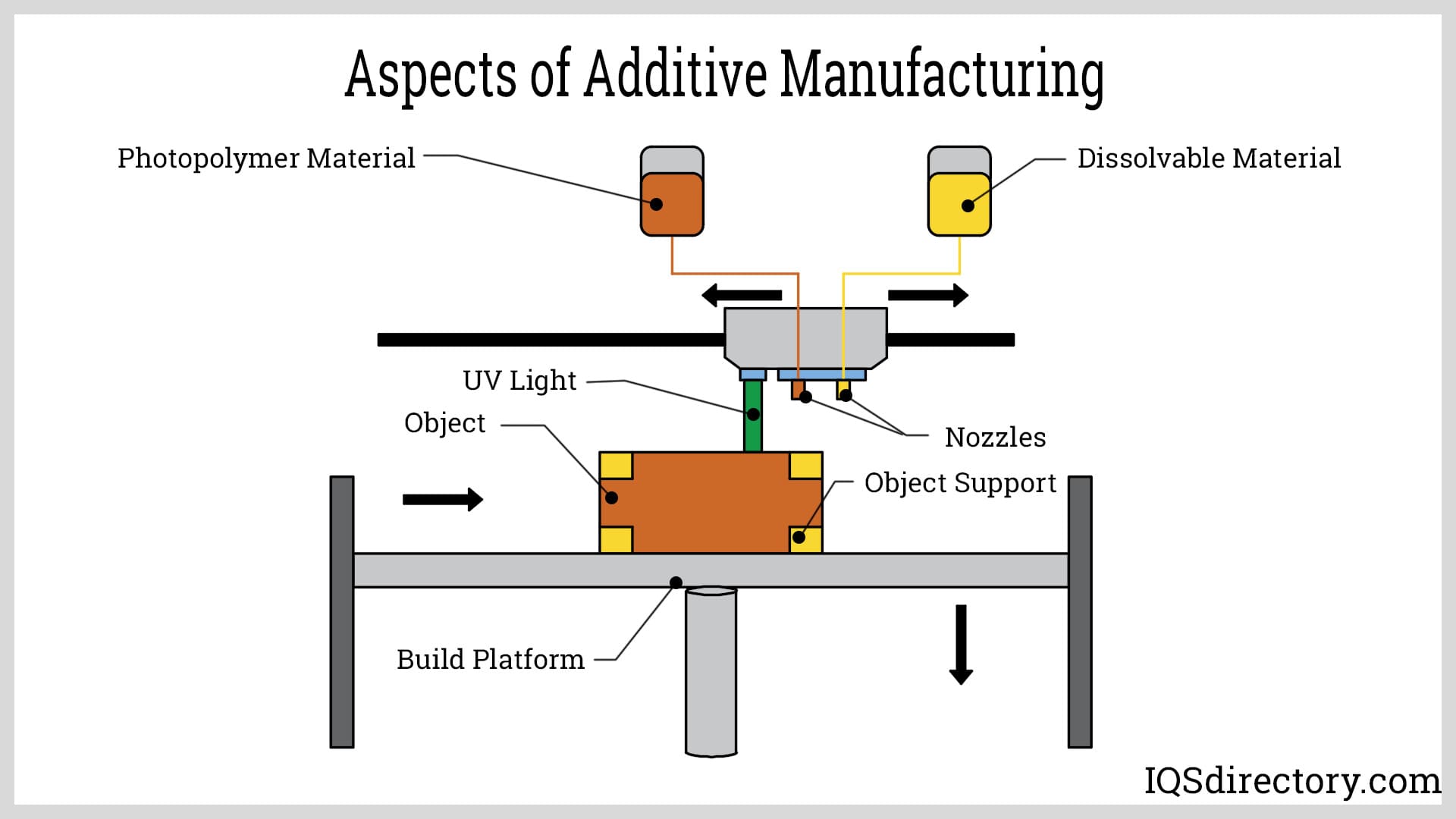

 Broaching
Broaching CNC Machining
CNC Machining Expanded Metals
Expanded Metals Laser Cutting
Laser Cutting Metal Etching
Metal Etching Metal Fabrication
Metal Fabrication Perforated Metals
Perforated Metals Screw Machine Products
Screw Machine Products Metal Stampings
Metal Stampings Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tube Fabrication
Tube Fabrication Water Jet Cutting
Water Jet Cutting Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services